Overview of IP Address
What is an IP Address?
An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. It serves two main functions: identifying the host or network interface and providing the location of the device in the network. IP addresses come in two versions: IPv4, which is a 32-bit number represented as four decimal numbers separated by periods, and IPv6, a 128-bit number, which is expressed in hexadecimal and separated by colons. The IPv4 address is the most commonly utilized format, while the larger IPv6 addresses have been developed to meet the growing need for IP address space due to the increasing number of devices connected to the internet.
Importance of Knowing Your PC’s IP Address
Knowing the IP address of a computer is crucial for various tasks, especially in networking and troubleshooting connectivity issues. When you connect to a network, whether at home, a school, or a workplace, your device is assigned a local IP address, which is essential for routing data within that network. In cases of network problems, knowing your IP address can simplify the diagnosis process since network administrators might require the address to identify devices on their network.
Furthermore, understanding your IP address can enhance security. Using a VPN or changing one’s IP address can help to mask a user’s physical location, making it harder for malicious actors to track online activity. In addition, when setting up servers or running services that require interaction with other users or devices on a network, sharing the IP address is often necessary for establishing direct communication.
In a larger context, knowing one’s public IP address can be helpful for remote access to systems or services. Many users require access to specific services that rely on an existing connection to their home network, often necessitating the public IP for port forwarding or remote desktop applications. Overall, having the knowledge of how to locate both local and public IP addresses is beneficial for everyday internet navigation and managing connections effectively.
Steps to Find IP Address on Windows 10
Opening Command Prompt
To locate the IP address on a Windows 10 machine, the first step involves accessing the Command Prompt. This can be accomplished by clicking the Start icon located in the taskbar. Once the Start Menu appears, the user should type “command prompt” into the search bar. After entering the search term, they should press the Enter key, which will open the Command Prompt window. In some cases, right-clicking the Start button may provide a quicker access point to this utility.
Running ipconfig /all Command
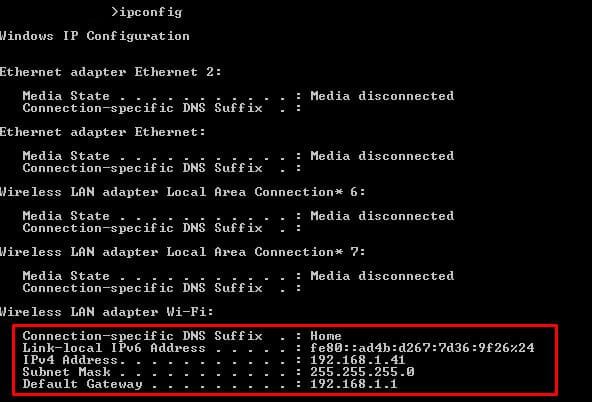
Once the Command Prompt is open, the user needs to type the command “ipconfig /all” and then press Enter. It is important to note that there is a space between “ipconfig” and “/all.” This command will produce a list of all network configurations associated with the computer. The output will present various pieces of information, including the IPv4 address, subnet mask, and default gateway. The IPv4 address, which is generally the address most needed when troubleshooting or configuring network settings, will be displayed under the section for the active network connection, such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi. The address will be listed next to “IPv4 Address” and will follow the standard format, typically written as four sets of numbers, such as 192.168.1.1. Verifying the context in which the address appears is essential, especially when there are multiple network adapters or virtual connections present on the machine. This process enables a clear identification of the correct IP address needed for any necessary connections or configurations.
Locating Ethernet Card IP Address
Identifying Ethernet Adapter Title
To find the IP address associated with the Ethernet card, users should first examine the information displayed in the Command Prompt output after executing the “ipconfig /all” command. The output contains various connection types and their associated details. Look for the section titled “Ethernet Adapter” in the list presented. This section provides specific information about the wired connection. The user may encounter multiple Ethernet adapters if other network interfaces are present, such as virtual adapters or additional network interfaces created by software like virtualization tools. It’s crucial to focus on the Ethernet adapter that corresponds to the active network connection to obtain accurate information. Identification of the correct adapter is vital for ensuring the right IP address is being configured or referenced.
Finding IPv4 Address for Ethernet Card
Once the user has located the Ethernet adapter section, the next step is to find the IPv4 address associated with that connection. The IPv4 address will be explicitly labeled in the output following the term “IPv4 Address.” Typically, this address appears in a standard numerical format composed of four sets of numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.1.10. In addition to the IPv4 address, users may also find details concerning the subnet mask and the default gateway of the network they are connected to. The subnet mask usually assists in determining which portion of the IP address refers to the network versus the individual device. Understanding these specifics is essential, especially during troubleshooting networking issues or setting up a new connection.
For Windows 10, users should ensure that they are checking the results under the correct section of the output, emphasizing the connection they are actively using—either through Ethernet or Wi-Fi. In cases where multiple connections are active, extra attention should be given to the Ethernet adapter section, making it easier to differentiate between various connections. This method provides an efficient way for users seeking to establish a solid understanding of their network configuration, enabling proactive management of their devices and connections. It empowers users with the knowledge needed to delve into the details of their network settings and ensure seamless connectivity.
Locating Wireless Card IP Address
Recognizing Wireless LAN Adapter Title
To locate the IP address associated with a computer’s wireless card, users first need to navigate the information displayed after executing the “ipconfig /all” command in the Command Prompt. In the output, one can identify the section labeled “Wireless LAN Adapter.” This segment contains pertinent information related to the computer’s wireless network connection. It is vital to distinguish this section from others like “Ethernet Adapter” to ensure that one is examining the correct interface. For those who have multiple adapters or virtual connections present, this step is crucial for avoiding confusion. Any descriptor containing the term “Virtual” should be disregarded, as it does not pertain to the physical wireless connection required for typical internet access.
Locating IPv4 Address for Wireless Card
Once the “Wireless LAN Adapter” section is identified, users should look for the entry titled “IPv4 Address.” This designation reveals the actual IP address assigned to the wireless network card. Typically, the IPv4 address will follow the standard numerical format, which consists of four sets of numbers separated by periods, such as 192.168.0.1. Knowing this address is essential for network troubleshooting and configuration, as it enables connections to the correct device on the network. When documenting this address, users must ensure that they note any labels or titles to verify the IP address accurately corresponds to the wireless connection rather than other possible entries which may originate from different connections or attributes of the machine. This attention to detail aids in maintaining clarity, especially in devices that continuously connect to disparate networks.
Understanding Host Name IP Address
Definition of Host Name IP Address
The host name IP address is a unique identifier assigned to a device connected to a network. It serves two primary functions: identifying the device and ensuring communication between devices on a network or the internet. A host name is a human-readable label that corresponds to the numerical IP address, making it easier for users to remember and access devices. For example, the IP address may be represented as a series of numbers, such as 192.168.1.1, while the host name could be something like “mycomputer.local.” This distinction helps simplify the user experience, allowing individuals to connect with devices through intuitive names instead of complex numerical addresses. By converting these numerical IP addresses into host names, the technology behind domain name systems (DNS) facilitates the seamless operation of internet browsing and local network connections.
How to Determine Host Name IP Address
To determine a device’s host name IP address, one can utilize various methods, depending on the operating system in use. For Windows users, the Command Prompt serves as a straightforward tool. After opening the Command Prompt, the user can type the command “ipconfig” to display the IP configuration details, including the host name and IP address. For instance, the output will typically include the device’s IPv4 address alongside its host name, enabling the user to easily map the known name to the respective numerical address.
On macOS, users can find their host name IP address by accessing the System Preferences and selecting the Network option. Within the Network settings, the device’s status will reveal both the IP address and the respective host name. This information is vital for troubleshooting connectivity issues, allowing users to verify if the correct IP address corresponds to the specified host name.
For enthusiasts working with networking tools, advanced options such as the ping command can also be employed to resolve host names to their corresponding IP addresses. By entering “ping [host name]” in the Command Prompt or Terminal, users can trigger the system to identify the designated IP linked to the host name. This technique is particularly useful for network diagnostics and assessing connectivity between local devices or external servers.
By utilizing these straightforward methods, users can efficiently determine their host name IP address, facilitating smoother communications and ensuring proper network configurations.
Discovering Physical Address of Your Machine
Importance of Physical Address
The physical address of a machine, often referred to as the MAC (Media Access Control) address, is crucial for identifying devices on a network uniquely. While an IP address may change based on the network configuration, the MAC address remains constant for a physical network interface. This makes the MAC address vital for network security and management, as it can be used to grant or restrict device access to the network. Additionally, understanding the MAC address is essential for diagnosing connectivity issues or interacting with network equipment such as routers and switches. In environments where network efficiency is paramount, knowing how to find this address can facilitate better troubleshooting and overall smoother operations.
Steps to Find Physical Address
To find the physical address of a machine running Windows, users can follow a straightforward process using either the Command Prompt or the graphical user interface. First, they can open the Command Prompt by searching for “cmd” in the Start Menu. Once the Command Prompt window appears, typing the command “ipconfig /all” provides a comprehensive view of all network configurations, including the physical addresses of each network adapter.
In the Command Prompt output, users should scroll to find the section labeled with the name of their network adapter, which could be either Ethernet, Wireless LAN, or another installed interface. Within this section, the line that states “Physical Address” or “MAC Address” displays the value they need. The address will be presented in six pairs of hexadecimal digits, typically separated by hyphens or colons, such as 00-1A-2B-3C-4D-5E.
Additionally, for users who prefer a visual method, they can access the Control Panel on their Windows machine, navigating through the following path: Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. After selecting “Change adapter settings,” they can right-click on their active network connection and choose “Status.” In the Status window, clicking on “Details” will reveal the physical address alongside other network information. This method offers a user-friendly alternative to the Command Prompt, making it suitable for users less familiar with command-line interfaces.
For Mac users, finding the MAC address requires similar steps through the System Preferences. By selecting “Network” and then the appropriate connection, the physical address can be viewed under “Status.” Using these methods, individuals can efficiently identify their machine’s physical address, which is essential for network management and troubleshooting tasks.
Troubleshooting IP Address Issues
Common Problems with IP Address
There are several issues that users might encounter with their IP addresses, affecting their ability to connect to the internet or communicate with devices on a local network. One common problem is an IP address conflict, which occurs when two devices on the same network are assigned the same IP address. This situation leads to connectivity problems for one or both devices, preventing them from properly accessing the network. Another frequent issue is the dynamic assignment of IP addresses through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). Sometimes, devices may not receive an IP address, leaving them with a self-assigned IP, which usually falls within the range of 169.254.x.x, indicating they are not connected to the network as intended.
In addition to these, users may also face problems with their firewall or security software blocking network connectivity. These applications may mistakenly identify network traffic as a potential threat, thus disrupting the communication between devices. Outdated network drivers can also cause problems, resulting in devices misreporting their IP configurations or failing to connect to the network at all. Lastly, when a user changes their network configuration, such as switching from a wired connection to wireless, they might experience temporary connectivity disruptions due to mismatched IP settings or configurations.
Solutions for IP Address Connectivity Issues
To resolve IP address issues, users can start by performing a few basic troubleshooting steps. First, they should restart their device and the router or modem, as this can often fix temporary connectivity problems. If the issue persists, accessing the Command Prompt and entering the command “ipconfig /release” followed by “ipconfig /renew” can force the device to request a new IP address from the DHCP server. This process can often rectify conflicts and misconfigurations.
If the device is showing a default IP address in the 169.254.x.x range, it indicates that it is not receiving an IP address from the DHCP server. In this case, checking the Ethernet cable or wireless connection settings is crucial. For wired connections, users should ensure that the cable is securely connected and not damaged. For wireless connections, confirming that the Wi-Fi is enabled and that the device is connected to the correct network can help.
Additionally, disabling any firewall or security software temporarily can identify if these applications are blocking the network connection. If the problem resolves after disabling them, users may need to adjust the settings to permit proper connectivity. Lastly, updating the network driver through the Device Manager can solve issues related to outdated software, ensuring the network adapter functions correctly and communicates seamlessly with the network.
Recap of Importance of Knowing IP Address
Knowing the IP address of a machine is essential for various reasons, including managing network connectivity and securing devices within a network. An IP address serves as a unique identifier for each device connected to a network, allowing for proper communication between devices and efficient data transfer. Without this address, devices might struggle to receive and send information accurately. In troubleshooting scenarios, obtaining the correct IP address can significantly aid in identifying connection issues, whether due to incorrect configurations, hardware malfunctions, or network performance problems. Furthermore, for network administrators, keeping track of device IP addresses helps maintain network security. They can monitor traffic effectively and restrict unauthorized access, ensuring that only recognized devices can connect to the network.
Final Thoughts on Managing Your PC’s IP Address
Efficiently managing a PC’s IP address involves several key practices. Users regularly renew their IP addresses by rebooting routers or manually refreshing connection settings, helping avoid IP conflicts, especially in DHCP configured networks. For environments where static IP addresses are preferable, users might consider configuring their machines to maintain a fixed address, preventing disruptions during connectivity. Additionally, using command-line tools like Command Prompt or PowerShell can streamline the process of checking and modifying IP address settings. Users are encouraged to familiarize themselves with these tools, as they offer quick insights into network configurations. Moreover, knowledge of both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses is advantageous as networks continue to evolve towards IPv6 adoption, allowing for more extensive address availability. In cases where privacy concerns arise, utilizing a VPN can obscure a device’s public IP address, safeguarding user identity online. Networking tools and security software can also enhance device management, providing an organized approach to monitor device connectivity and performance.